what structure returns blood from the lungs to the heart?
Heart and Circulatory Organisation
What Does the Heart Do?
The heart is a pump, commonly beating near threescore to 100 times per infinitesimal. With each heartbeat, the heart sends blood throughout our bodies, conveying oxygen to every cell. Afterwards delivering the oxygen, the blood returns to the heart. The center then sends the claret to the lungs to pick up more oxygen. This cycle repeats over and over again.
What Does the Circulatory System Do?
The circulatory system is made up of claret vessels that behave blood abroad from and towards the middle. Arteries comport blood away from the heart and veins carry blood back to the heart.
The circulatory organisation carries oxygen, nutrients, and to cells, and removes waste matter products, like carbon dioxide. These roadways travel in ane direction but, to go along things going where they should.
What Are the Parts of the Middle?
The heart has four chambers — two on elevation and two on bottom:
- The ii bottom chambers are the right ventricle and the left ventricle. These pump claret out of the heart. A wall called the interventricular septum is betwixt the 2 ventricles.
- The 2 top chambers are the right atrium and the left atrium. They receive the blood entering the heart. A wall chosen the interatrial septum is between the atria.
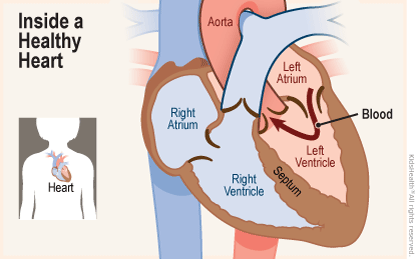
The atria are separated from the ventricles by the atrioventricular valves:
- The tricuspid valve separates the right atrium from the right ventricle.
- The mitral valve separates the left atrium from the left ventricle.
Two valves also split up the ventricles from the large blood vessels that conduct blood leaving the center:
- The pulmonic valve is between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, which carries blood to the lungs.
- The aortic valve is betwixt the left ventricle and the aorta, which carries blood to the trunk.
What Are the Parts of the Circulatory System?
Two pathways come from the center:
- The pulmonary apportionment is a brusque loop from the heart to the lungs and back once again.
- The systemic circulation carries blood from the heart to all the other parts of the body and back once more.
In pulmonary circulation:
- The pulmonary artery is a large artery that comes from the heart. Information technology splits into two main branches, and brings blood from the heart to the lungs. At the lungs, the blood picks upwards oxygen and drops off carbon dioxide. The blood and so returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins.
In systemic circulation:
- Next, claret that returns to the heart has picked up lots of oxygen from the lungs. So it tin now go out to the torso. The aorta is a large avenue that leaves the heart carrying this oxygenated claret. Branches off of the aorta send claret to the muscles of the heart itself, likewise equally all other parts of the body. Similar a tree, the branches gets smaller and smaller as they become farther from the aorta.
At each body office, a network of tiny blood vessels called capillaries connects the very small-scale artery branches to very small veins. The capillaries accept very thin walls, and through them, nutrients and oxygen are delivered to the cells. Waste matter products are brought into the capillaries.
Capillaries then lead into pocket-size veins. Small veins lead to larger and larger veins as the blood approaches the center. Valves in the veins proceed claret flowing in the correct direction. Ii large veins that lead into the eye are the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava. (The terms superior and inferior don't mean that ane vein is better than the other, but that they're located above and below the centre.)
Once the claret is back in the centre, it needs to re-enter the pulmonary apportionment and get dorsum to the lungs to driblet off the carbon dioxide and option up more oxygen.
How Does the Heart Shell?
The heart gets messages from the body that tell information technology when to pump more or less blood depending on a person'due south needs. For case, when you're sleeping, it pumps just enough to provide for the lower amounts of oxygen needed past your trunk at residuum. Simply when you're exercising, the heart pumps faster then that your muscles get more oxygen and can work harder.
How the eye beats is controlled by a organization of electrical signals in the heart. The sinus (or sinoatrial) node is a small-scale surface area of tissue in the wall of the right atrium. It sends out an electrical point to get-go the contracting (pumping) of the middle muscle. This node is called the pacemaker of the heart because it sets the rate of the heartbeat and causes the rest of the heart to contract in its rhythm.
These electrical impulses make the atria contract first. Then the impulses travel down to the atrioventricular (or AV) node, which acts as a kind of relay station. From here, the electrical signal travels through the right and left ventricles, making them contract.
One complete heartbeat is made up of two phases:
- The first phase is called systole (pronounced: SISS-tuh-lee). This is when the ventricles contract and pump blood into the aorta and pulmonary avenue. During systole, the atrioventricular valves close, creating the beginning sound (the lub) of a heartbeat. When the atrioventricular valves close, it keeps the claret from going back up into the atria. During this time, the aortic and pulmonary valves are open to let claret into the aorta and pulmonary avenue. When the ventricles finish contracting, the aortic and pulmonary valves close to forbid blood from flowing back into the ventricles. These valves closing is what creates the second sound (the dub) of a heartbeat.
- The second stage is called diastole (pronounced: dice-AS-tuh-lee). This is when the atrioventricular valves open and the ventricles relax. This allows the ventricles to fill with blood from the atria, and become ready for the adjacent heartbeat.
How Can I Help Keep My Center Healthy?
To help proceed your eye healthy:
- Get plenty of exercise.
- Eat a nutritious diet.
- Reach and go on a healthy weight.
- If you smoke, quit.
- Go for regular medical checkups.
- Tell the physician virtually any family unit history of eye issues.
Let the doctor know if you have any chest pain, trouble breathing, or silly or fainting spells; or if you lot experience similar your heart sometimes goes really fast or skips a beat.
Appointment reviewed: September 2018
Source: https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/heart.html
0 Response to "what structure returns blood from the lungs to the heart?"
Post a Comment